Veterinary advice should be sought from your local veterinarian before applying any treatment or vaccine. Not sure who to use? Look up veterinarians who specialize in poultry using our directory listing. Find me a Vet
Other Names: Sticktight Flea Infestation
| Bedbug | Red poultry mite | Sticktight Flea | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adult Appearance | |||
 |  |  | |
| Size | 4-12 mm (0.15-0.47 in) | 1-1.5 mm (0.04-0.06 in) | 1.5-4 mm (0.06-0.16 in) |
| Color | Reddish brown | Gray to black | Dark brown |
| Turns red | Yes | Yes | No |
| Wings | No | No | No |
| Body type | Oval and flat | Oval | Flat |
| Speed | Quick-moving | Slow moving | Slow moving |
| Visible to the naked eye | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Feeds on | Blood | Blood | Blood |
| Where they are found | Hide in crevices, cracks, behind floorboards, in walls, and behind wall outlets during the day, feed on chickens at night | Hide in crevices and cracks during the day, feed on chickens at night | Bare skin on the head - comb, wattles, near eyes |
| Transmission | Contaminated equipment | Wild birds, rodents, wildlife, dogs, cats, humans, contaminated equipment | Turkeys, wildlife, wild birds, dogs, cats, horses, pigs, people, soil, litter |
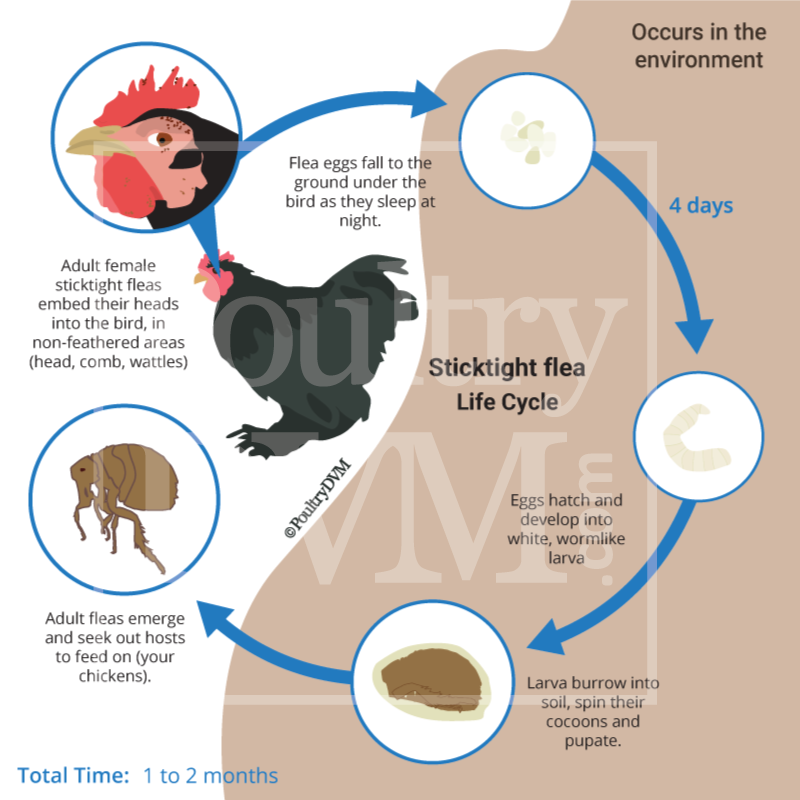
| Where eggs are laid | Tiny, microscopic whitish, sticky eggs that adhere to surfaces in secluded areas | Lays their eggs in their hiding spots | Lay their eggs around the eyes anad wattles of chickens, causing nodules. Once the flea larvae hatch, they drop off the chicken to live in the soil for 2 weeks. |
| Average Life cycle | 4 weeks | 2 weeks | 1-2 months |
| How you can tell | Look around the premises for the presence of bugs | Look for them at night on the birds | Visible during the daytime, found in clusters on unfeathered areas, such as the bird's eyes, comb, and wattles. |
| Temperature | Temperate regions | Warm weather | Warm and humid weather |
| Clinical signs | Excessive feather loss, vent irritation, lesions on breasts and legs, anemia, reduced egg production | Restlessness at night, dermatitis, anemia, may cause chickens to alter where they roost at night. | dark brown spots face, anemia, restlessness, swollen eyelids, crusted lesions, ulcerations, blindness |
| Zoonotic | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Carry diseases | Yes | Yes | No |
| Name | Summary | |
|---|---|---|
| Small numbers of fleas can be removed individually by hand using tweezers. Followed by applying an topical antibiotic ointment to the area where the flea was found to minimize risk of secondary infections. | M Ficken Texas A&M Veterinary Diagnostic Lab 2024; P Koehler 2015 | |
| Malathion 5% liquid or gel applied directly to the fleas | F Salgado 2017 | |
| Fipronil | Spray directly on fleas | B Speer; Clinical Veterinary Advisor |
| Spinosad (Trade name Elector PSP) | Applied as a spray directly on chickens and all coop housing components. | B Mullens 2017; A Murillo 2017; Dow AgroSciences 2001 |
| Sulfur | Applied as a dust to all housing components in coop | A Murillo et al., 2016, G Damerow |
| Permethrin | Applied as a powder (0.24% permethrin) or spray (3 ounces of 10% permethrin is mixed in a 5 gallon bucket of water) on all housing components. | G Damerow |
| Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn |
© 2026 PoultryDVM All Rights Reserved.