The Bobcat
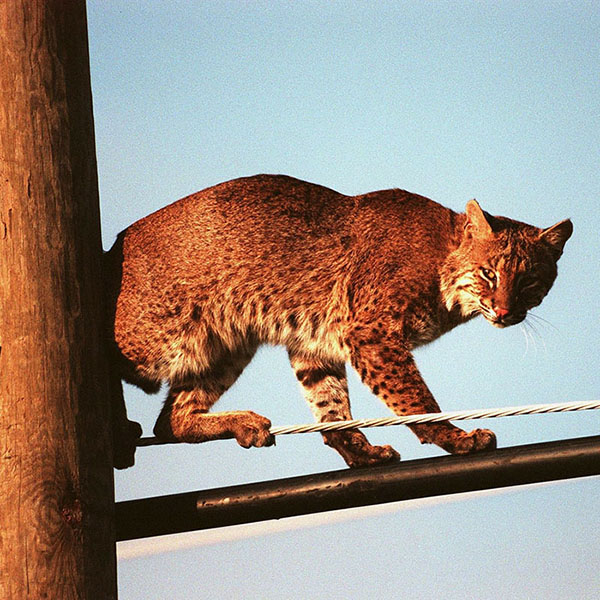
The bobcat (Lynx rufus) is an elusive, common predator of livestock. It comes from the same family as the domestic cat and cougar. Bobcats are secretive, shy, solitary, and seldom seen in the wild. They are active during the day but prefer twilight, dawn, or night hours. Bobcats are opportunistic predators, feeding on poultry, sheep, goats, house cats, small dogs, exotic birds, waterfowl, game animals and sometimes calves. Few predators other than cougars and humans are able to kill an adult bobcat.
Adult male bobcats weigh between 20 to 30 pounds. Bobcats can be various shades of buff and brown, with dark brown or black stripes and spots on some parts of the body. The tip of the tail and the backs of the ears are black. They have short ear tufts, and ruffs of hair on the side of the head, giving the appearance of sideburns.
Habitat
Bobcats seek shelter in rock cliffs, outcroppings, and ledges. When in wooded areas, they will live in large brush or log piles and hollow trees or logs.
Electrified : Install two electrified wires, 12 and 18 inches above ground and onto existing fence posts, poultry pen supports, and other structures using the proper insulators. A single strand of wire may be sufficient, but two wires will provide added insurance against climbing. Run one or two electrified wires towards the top of the fence to prevent bobcats from jumping the lower hot wires.
Tree access : Install a predator guard in areas where bobcats can climb a tree to gain access to poultry or other animals. Make sure the guard is at least 6 feet height.
Maintenance of property : Keep brush cut or sprayed and lawn regularly mowed
- Lighting : Use night lighting with white flashing lights, or bright continuous lighting.
- Loud noises : Play blaring music or recordings of barking dogs.
- Change of scenery : Make changes periodically to layout of area