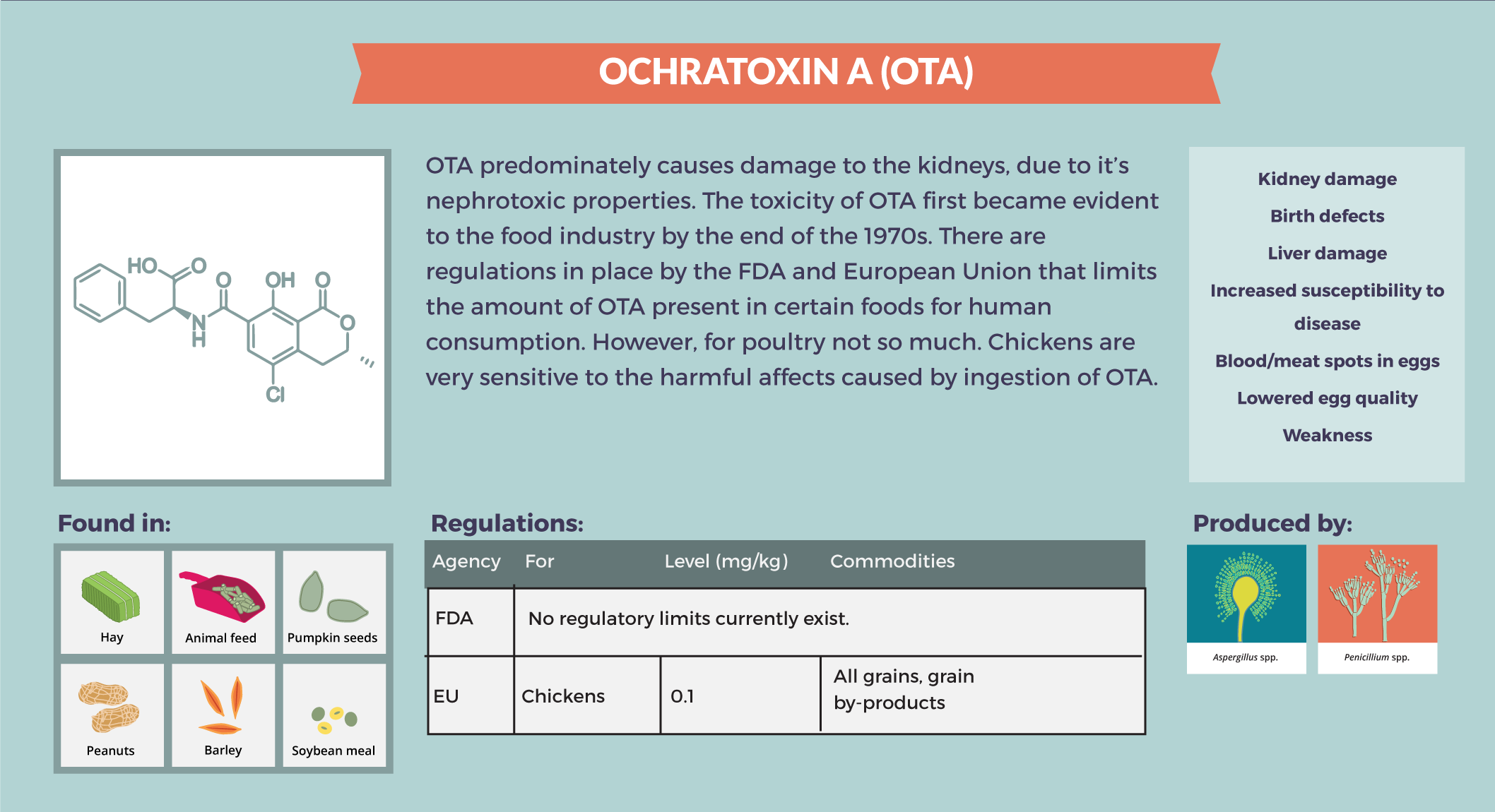
Ochratoxicosis is caused by ingestion of ochratoxin A (OTA), a type of mycotoxin, which has nephrotoxic, hepatotoxic, teratogenic, and immunotoxic effects on several animal species. Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites produced by a wide range of filamentous fungi which have adverse effects on humans, animals and crops that result in illnesses and economic losses. Mycotoxins are estimated to contaminate 25% of the world's grains that are used for food (FAO 2001), particularly in grains used as ingredients in commercial feed for livestock such as chickens. OTA is produced by different species of
Aspergillus and
Penicillium such as
A. ochraceus, A. carbonarius, P. verrucosum and
P. nordicum. However,
A. carbonarius is considered to be the main producer of OTA on coffee and grapes.
The resulting toxic effects of chickens consuming OTA contaminated feed include:
- Inhibition of protein synthesis
- Induction of lipid peroxidation
- Impairment of calcium homeostasis
- Oxidative stress
- DNA damage
- Increased incidents of food allergies
- Reduced blood coagulability
- Destruction of digestive enzymes
- Reduced immunity, leading to increased susceptibility to invasion by harmful pathogens
- Circulatory system damage
Recent research suggests that several Essential Oils (E.Os) have shown to be beneficial at inhibiting production of
A. carbonarius, the fungi responsible for producing OTA. The E.O of fennel (
Foeniculum vulgare), at 5 µL/mL was found to be the most effective.